If you’ve never been to Seed Savers Exchange near Decorah in the lovely Bluff Country of northeast Iowa, then you should. Especially as it is celebrating its 50th anniversary this year.
![]()
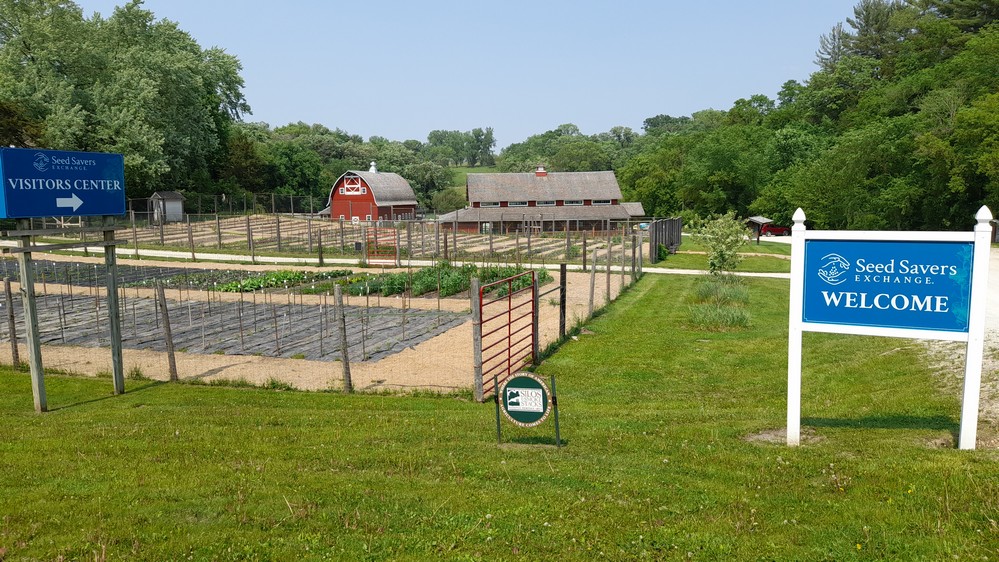

Founded in 1975 (originally as True Seed Exchange) by Kent and Diane Ott Whealy in Missouri, Seed Savers Exchange is a tax-exempt 501(c)3 non-profit that conserves and promotes America’s culturally diverse but endangered garden and food crop heritage for future generations by collecting, growing, and sharing heirloom seeds and plants.
In this video, Diane Ott Whealy describes how it all began.
Seed Savers Exchange moved to Decorah in 1987, when the Whealys bought a parcel of land, which became Heritage Farm.
Over five decades, Seed Savers Exchange has built an impressive community (in reality a movement) of gardeners and seed stewards, sharing and swapping unique varieties you might not find anywhere else, combining in situ conservation in home gardens and ex situ in the seedbank at Decorah.
 Varieties such as these (of the many thousands in the Exchange network and collection):
Varieties such as these (of the many thousands in the Exchange network and collection):
- Cherokee Trail of Tears, a snap bean carried by the Cherokee over the Trail of Tears, the infamous death march from the Smoky Mountains to Oklahoma in 1838-39);
- Bull Nose Bell, a sweet pepper introduced into North America in the 1700s, and grown by elder statesman and third POTUS, Thomas Jefferson, in his garden at Monticello in 1812);
- or the tomato variety German Pink (one of two varieties that started it all – the other being Grandpa Ott’s, a morning glory) introduced into the USA from Bavaria in the late 19th century. Both are featured on the covers of The Exchange 2025 Yearbook and The 2025 Seed Catalog.
There’s lots to see and do at Seed Savers Exchange (click on the image below – and others with a red border – to open a larger version) and visitors are encouraged to hike the trails, and explore the 890 acre farm.
When the apples are ripe in the Historic Orchard, visitors may pick their own. Local cider producers make a beeline to harvest and collect windfalls.
But Seed Savers Exchange is not all plants. The Ancient White Park cattle were introduced into the USA from the UK during WWII as a safeguard against loss of this ancient breed. Several herds were established, two ending up in Decorah. Coincidentally, not far from where we are now living in the northeast of England, there is a completely feral (but enclosed) herd of these beautiful cattle at Chillingham.
During our recent trip to the USA, Steph and I enjoyed a day-long visit to Seed Savers Exchange, staying a couple of nights in Decorah. It was an easy drive south from St Paul, MN (just under 160 miles, and about 3.5 hours on a sunny Sunday afternoon).
 A visit to Seed Savers Exchange was first mooted in May 2024, but having just made a long road trip across Utah and Colorado, I really didn’t want to get behind the wheel again. However, we had no epic road trip plans this year, so I decided to contact Executive Director, Mike Bollinger (right) last February to set up a visit.
A visit to Seed Savers Exchange was first mooted in May 2024, but having just made a long road trip across Utah and Colorado, I really didn’t want to get behind the wheel again. However, we had no epic road trip plans this year, so I decided to contact Executive Director, Mike Bollinger (right) last February to set up a visit.
Regular readers of my blog will know that Steph and I first became part of the germplasm conservation movement in the early 1970s. I spent much of my career in international agricultural research and academia, collecting farmer varieties of potatoes across the Andes of Peru, and in the Philippines managing the world’s largest genebank for rice at the International Rice Research Institute.
 So I asked Mike if we could have a ‘behind-the-scenes’ visit (not open to regular visitors), to learn about the organization in detail, and the management of such a large and diverse collection of plant species. He quickly agreed, and asked Director of Preservation, Michael Washburn (right) to set up a program for us.
So I asked Mike if we could have a ‘behind-the-scenes’ visit (not open to regular visitors), to learn about the organization in detail, and the management of such a large and diverse collection of plant species. He quickly agreed, and asked Director of Preservation, Michael Washburn (right) to set up a program for us.
In this post I’m not going to describe how Seed Savers Exchange works with its members, and how they share seeds among the community or from the seedbank. That information is available in detail on this section of its website.
 Incidentally, Seed Savers Exchange also has a commercial arm (which supports its non-profit mission), selling seeds through an annual catalog of around 600 or so varieties of vegetables, herbs, and flowers, some of which come from the collection.
Incidentally, Seed Savers Exchange also has a commercial arm (which supports its non-profit mission), selling seeds through an annual catalog of around 600 or so varieties of vegetables, herbs, and flowers, some of which come from the collection.
Michael introduced us to the preservation team (see below), and we spent time with each as well as having a very informative round table discussion where we shared our different perspectives and experiences in seed conservation.
Let me highlight some fundamental differences between managing (as I did) the rice collection at IRRI and the collection at Seed Savers Exchange.
IRRI’s collection of rice has its own complexities due to its size and the origin of the germplasm from many countries, with conservation and exchange subject to the rules of the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture.
On the other hand, Seed Savers Exchange is a voluntary non-profit, operating within the USA, and not subject to the same bureaucratic constraints. However, its complexity lies with the number of species conserved (and their conservation needs), as well as catering to the needs of the many members in the Exchange network.
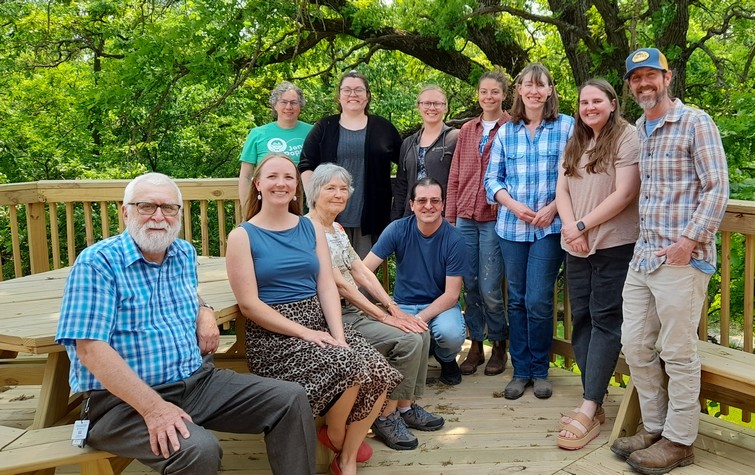

Standing (L-R): Heidi Betz (seed bank inventory technician), Maddison MacDonald (potato tissue culture lab manager), Briana Smorstad ( seed bank manager), Jamie Hanson (orchard manager), Sara Straate (seed historian), Natalie Aird (seed bank inventory coordinator), and Michael Washburn. Kneeling: Eduardo Fernandez (assistant seed historian). Seated (L-R): me, Josie Flatgrad (membership and exchange coordinator), and Steph.
Seed bank manager Briana Smorstad explained that the Seed Savers Exchange Collection has around 20,000 accessions (although the database lists many more that are no longer available). About 6000 (about 30% of the collection) are distributable accessions.
This is the scope of the collection, as defined in its 2013 Accessions Policy (updated in 2020):

As with any genebank, this one has its issues with ‘duplicate’ varieties (some with the same name but not necessarily the same variety, and others with different names) currently estimated at around 21% of the collection. Fortunately, and as we all agreed in our round table, Seed Savers Exchange does have a comprehensive database (developed in Microsoft Access) that keeps track of all the germplasm, its status, and where it actually sits in the cold stores (so can be quickly accessed). In the past year, some 4922 varieties were offered through the Exchange. However, if one of the members is listing any variety the Decorah team don’t list these for distribution.
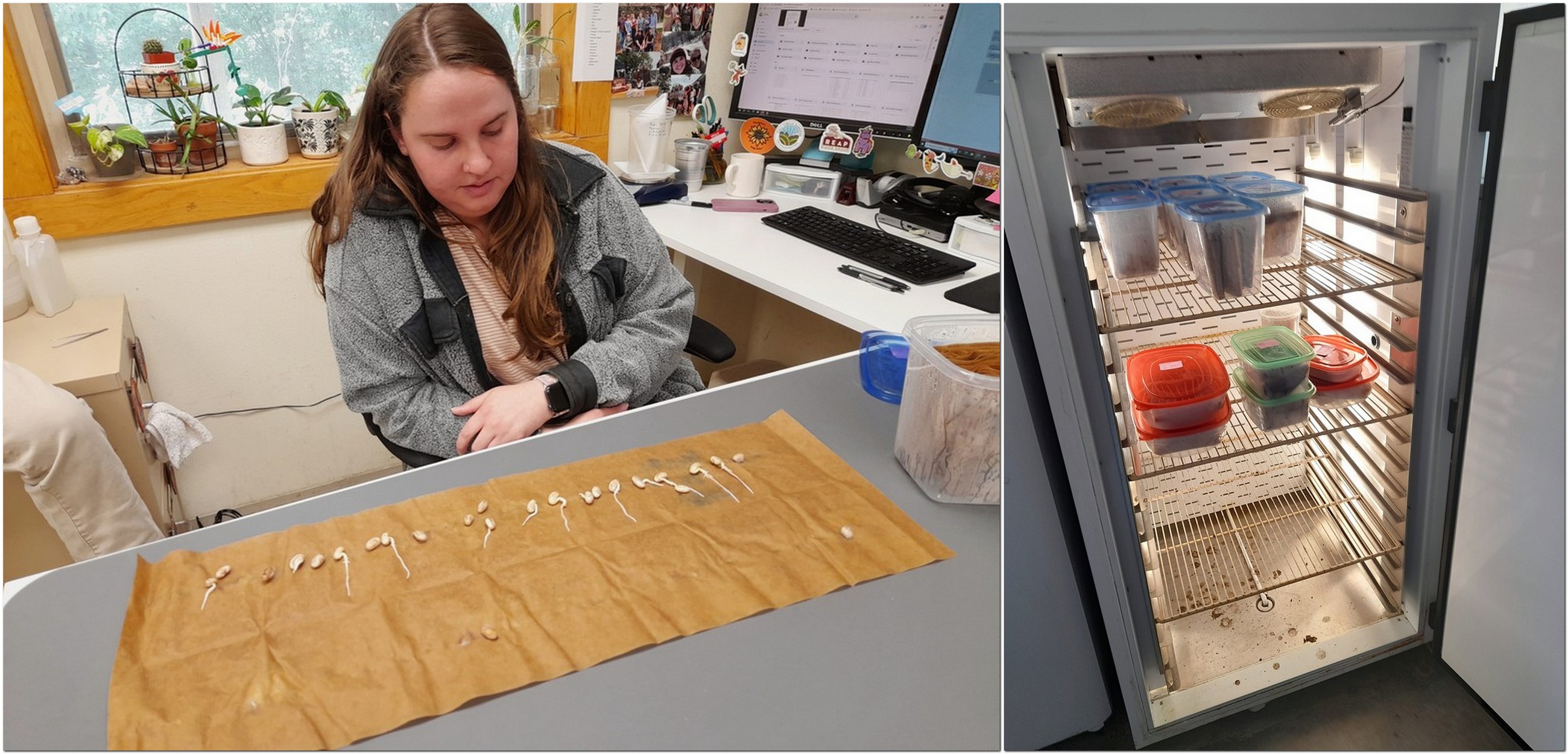
Natalie Aird, the seed bank inventory coordinator (who showed us the database) handles the seed quality assessments, running routine germination tests according to well-established protocols. And these important data guide how and when seeds become available for distribution.
We were especially privileged to be shown the base collection cold store (at around -18°C).
A recent initiative was launched, known as the L-to-D Project (Legacy to Distribution) which has moved 70 varieties in the collection into the Exchange.
The collection has Distributable or D varieties with sufficient seeds to meet regular requests through the Exchange. To have enough seeds means regeneration and multiplication on the Heritage Farm, which is time-, space, and labor-intensive. However, a whole series of seed packets or Legacy (L) accessions were identified in the collection, which were tested for quality and germination, and if reaching the desired standard were moved on to the D list, as was the case with the 70 varieties mentioned above. The project is described in more detail here.
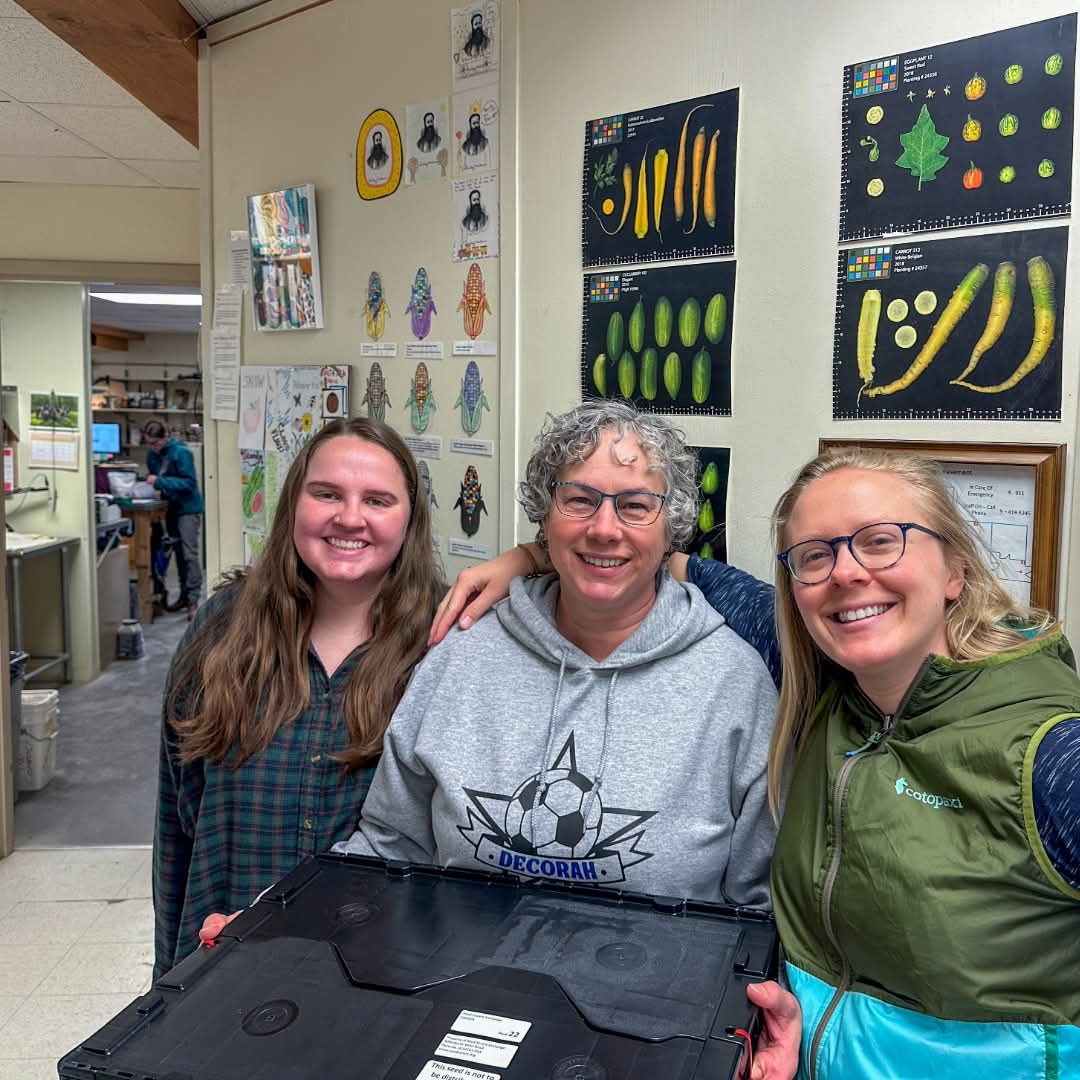
And to safeguard the collection decades into the future, Seed Savers Exchange has sent seeds to the Svalbard Global Seed Vault every year since the vault was first opened in 2008. Here’s a brief report from a Crop Trust news article in early June.
Here are the seedbank team (L-R, Natalie, Heidi, and Briana) preparing to send seeds to Svalbard earlier this year.

Seed Savers Exchange faces particular challenges with two components of its collection, namely the potato varieties, and the apple trees in the Heritage Orchard, which are maintained vegetatively.
In the case of potatoes, curated by Maddison MacDonald, there are 18 US heirloom varieties, 72 historic heirloom varieties, 10 exchange heirlooms. But the number of accessions is much higher. All maintained a virus-free tissue cultures. Potato varieties are distributed as tissue cultures, illustrated below.
One of the collection advisers (and former head of the genebank at the International Potato Center) Dr David Ellis has identified a group of 53 varieties (a core, so-to-speak) that represent the genetic diversity of the whole potato collection. But there is almost no overlap with the heirloom varieties mentioned earlier. The heirloom varieties meet the strict acquisition criteria for the collection and therefore have the highest priority. Managing a smaller number of priority varieties would permit greater focus on those. And, quite independently from David Ellis, I did suggest that Maddison should consider converting many of the other varieties to true potato seed, and in this way conserving the genetic diversity of the collection if not the individual clones.
The collection has an apple orchard with 1042 trees, consisting of 337 unique named varieties, managed by Jamie Hanson (below) and an assistant.

But there are duplicate trees, and these have been identified by DNA fingerprinting through Washington State University’s MyFruitTree initiative (at a cost of just $50 per sample). For example, fingerprinting has identified seven Bethel trees in the orchard, which will permit, in the future, removal of duplicate trees as part of orchard management. Jamie also curates a legacy grape breeding collection from the University of Minnesota.
I was particularly impressed by the outreach program involved in distributing apple varieties, whereby online tuition in grafting is given and the necessary tools also sent with the rootstocks and scions.
 Besides conserving the seeds and vegetatively-propagated species at Seed Savers Exchange, there is also coordination of the membership and Exchange (the gardener-to-gardener seed swap) a role that falls to Josie Flatgrad (right).
Besides conserving the seeds and vegetatively-propagated species at Seed Savers Exchange, there is also coordination of the membership and Exchange (the gardener-to-gardener seed swap) a role that falls to Josie Flatgrad (right).
Each year the Yearbook is published, a comprehensive tome of 474 pages! What a treasure trove of germplasm detail.
It has all the listings of varieties (this link explains how to read the listings) available from members, Seed Savers Exchange, details of the person offering seeds (some of whom have been listing seeds for more than 30 years), as well as a description of each variety. And to illustrate, here is the listing for Cherokee Trail of Tears (and also its catalog description) offered by members in California, Missouri, Oklahoma, Wisconsin, and Ontario.
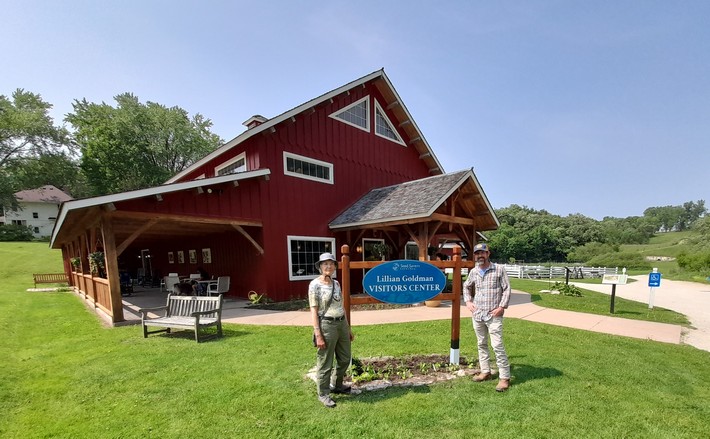
Following a lively round-table discussion with everyone who we met, Steph and I toured the Lillian Goldman Visitors Center (named after the philanthropist whose daughter Amy Goldman Fowler is a Special Advisor to Seed Savers Exchange Board of Directors), and the Iowa heritage barn (beside which Grandpa Ott’s morning glory were just beginning to climb), and the lovely garden in front that Diane Ott Whealy designed and looks after.

We are extremely grateful to Mike Bollinger and the whole Seed Savers Exchange team for their hospitality, their collegiality, and open discussions. We thoroughly enjoyed our six hours at Seed Savers Exchange, and hope to visit again in the future. And even though I spent most of my career in genetic conservation and use, I learned much that was new to me on this visit. It was an experience I shall cherish.
But let me finish this post by pointing you to this page on the Seed Savers Exchange website where there are numerous stories about a range of heirloom varieties and some of the stewards who make conservation of these varieties possible.
Inspirational indeed!







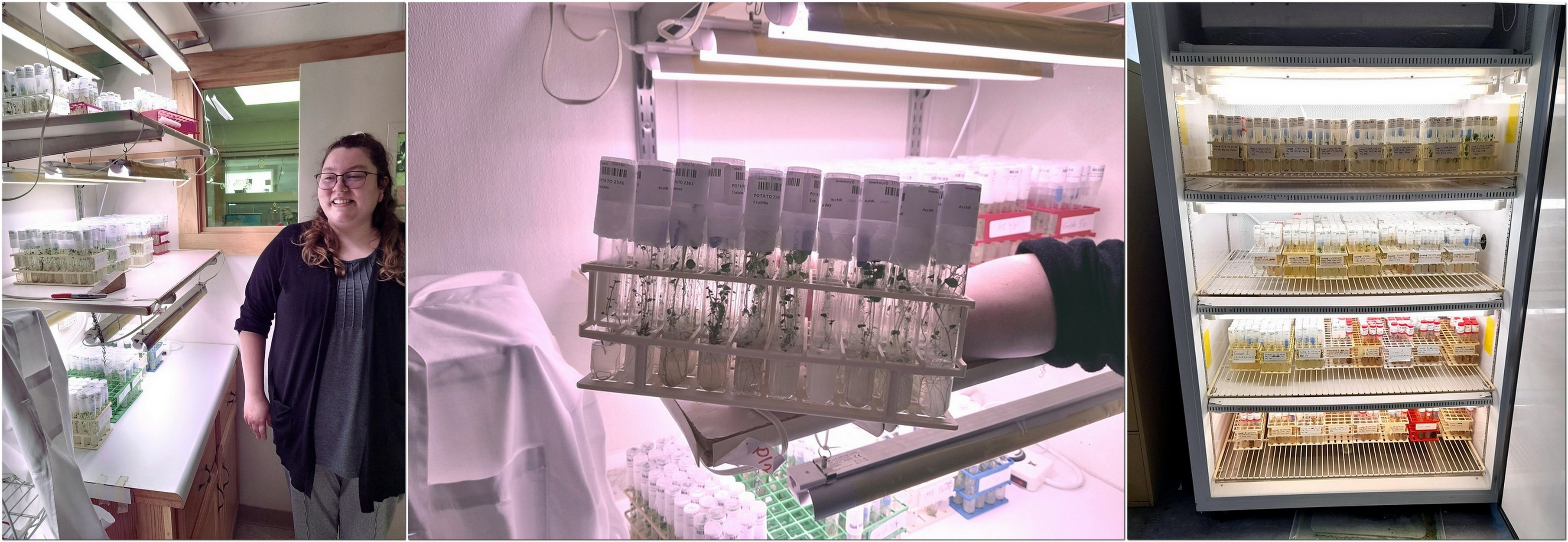





That’s quite an operation, bigger than Garden Organic maybe.
Sent from Outlook for iOShttps://aka.ms/o0ukef
LikeLike