I guess many folks south of the Watford Gap (often seen as the gateway between Northern England and Southern England) would have seldom if ever heard of Barnard Castle, a small market town in County  Durham in the northeast of the country.
Durham in the northeast of the country.
That is until May 2020 (during the height of the Covid-19 pandemic) when Dominic Cummings (right), a political strategist and chief adviser to then Prime Minister Boris Johnson was accused of breaking the strict lockdown regulations. Having taken his family north to County Durham from London (over 270 miles) in mid-April to stay with his parents, the family drove 30 miles to Barnard Castle to test—so Cummings claimed in a press conference—whether he was well enough to drive, having some problems with his eyesight. Since the majority of the population had isolated as required, Cummings’ apparent breach of the lockdown rules caused quite a scandal.
 Even the local optician, Specsavers (whose strapline is ‘Should have gone to Specsavers‘) got in on the act offering free eye tests for anyone visiting the town. Needless to say that the visit Steph and I made to this delightful Durham town a couple of weeks ago was not for an eye test.
Even the local optician, Specsavers (whose strapline is ‘Should have gone to Specsavers‘) got in on the act offering free eye tests for anyone visiting the town. Needless to say that the visit Steph and I made to this delightful Durham town a couple of weeks ago was not for an eye test.
No, we were there to explore the medieval castle built on a craggy outcrop overlooking the River Tees, as well as the ruins of Egglestone Abbey just a couple of miles southeast from the town center. And we planned a drive home over the glorious moorland between Teesdale and Weardale.
And we couldn’t have asked for better weather.

There is a comprehensive description and chronology of the castle’s history on the English Heritage website, so I am not going to elaborate further here, save to post the introduction on that particular page:
Barnard Castle was begun soon after 1093 on a dramatic site above the river Tees.
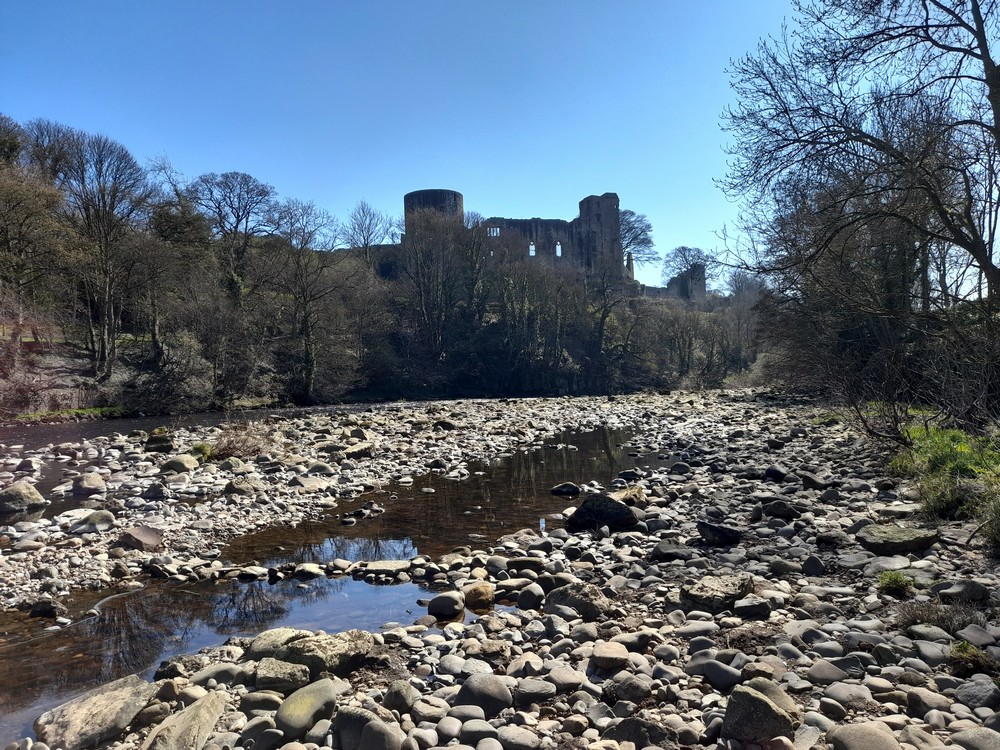

The castle was built to control a river crossing between the Bishop of Durham’s territory and the Honour of Richmond. Much of the present castle was built during the 12th and early 13th centuries by the Balliol family. The clifftop inner ward shows the remains of fine domestic buildings, including a magnificent round tower of around 1200.

From the 14th century onwards, the castle belonged to the earls of Warwick, and from 1471 to 1485 to the Duke of Gloucester, later Richard III.
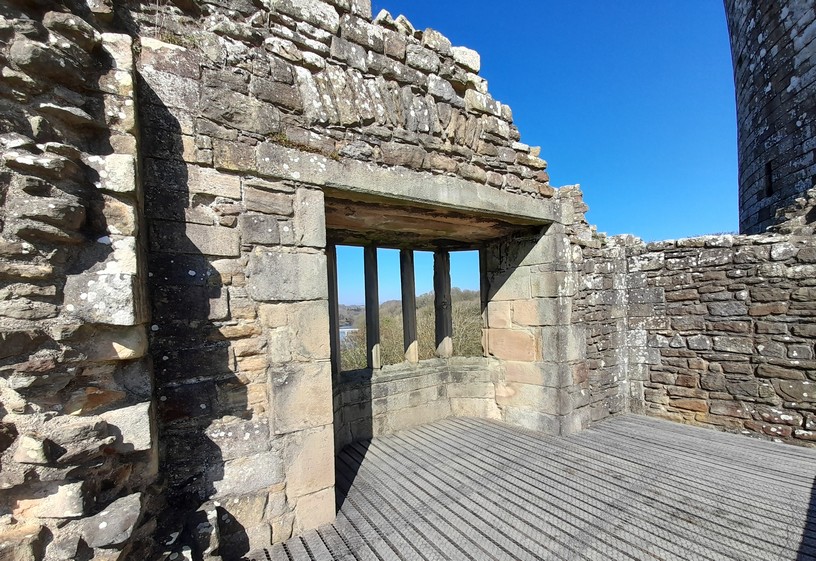
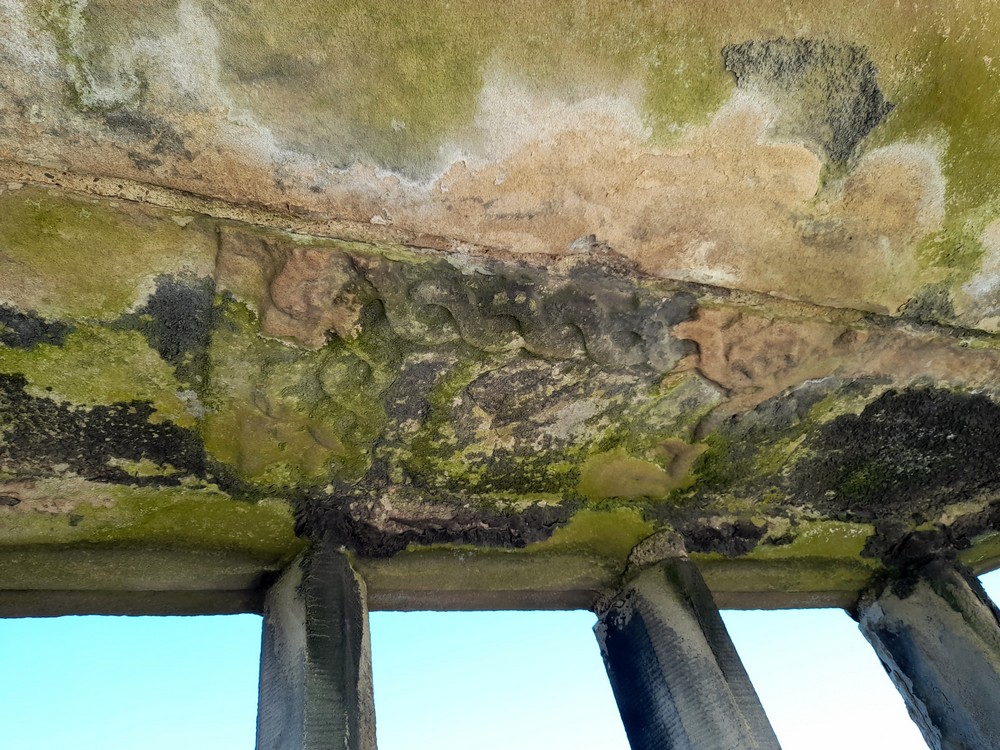


This is the remains of the image of Richard III’s boar above the oriel window.
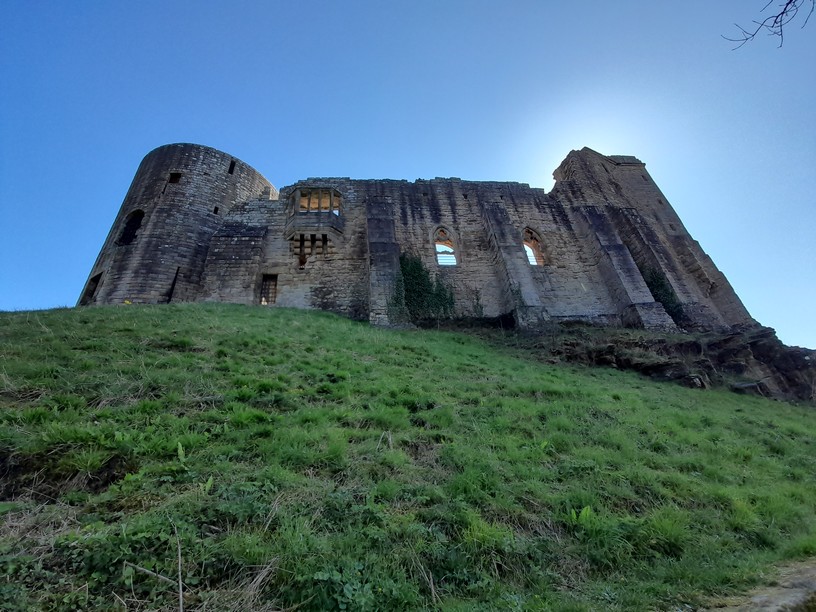

The round tower and oriel window from below.
After a fierce siege in 1569, when the castle was bombarded by rebels, the castle went into steep decline and was effectively abandoned by the early 17th century. It has remained an imposing ruin ever since.
Richmond Castle is just 15 miles southeast, and Middleham Castle (the boyhood home and northern stronghold of Richard III) is another 11 miles south.
Before heading to Barnard Castle, a neighbour had mentioned there was little to see there. Perhaps the ruins of the castle are not as extensive as others we have visited, but all around the site, English Heritage has placed explanatory information boards that put everything in perspective. And the young employees on reception were most helpful in pointing out different points of interest, and where precisely to view the Richard III boar!
The layout of the castle is a series of courtyards or wards, enclosed in a curtain wall, with the strongest and best fortified being the Inner Ward surrounding the Round Tower, Great Hall, and ancillary buildings like the bakery. The Inner Ward was also protected on two sides by the Great Ditch, and of course on the others by the cliff on which the castle had been built.
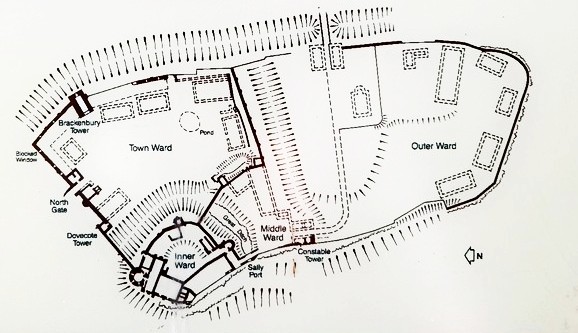
Entering through the main or North Gate, the expanse of the Tower Ward stretches to the Outer Ward.
The Great Ditch is rather impressive, and the Inner Ward is protected by a huge wall across the ditch.
What particularly impressed me about the Round Tower was the beauty of the dressed stone which covers the outer surface. English Heritage has opened the narrow stairs around the tower that take you up to the upper levels, with interesting views inside. Of course all the floors have long disappeared.
You can see the complete album of photos (together with images of the information boards) here.
After a walk down to the river so we could observe the castle in all its splendour on top of the crag, we headed back into the town, passing again past the impressive butter market (officially the Market Cross) built in 1747. It’s had several uses including town hall, fire station, prison, and dairy market.
I should add, for the benefit of anyone contemplating visiting Barnard Castle, that it is a busy town. There is no English Heritage parking at the castle. We parked at the long-term Queen Street car park (cash, cards, and app payment), £1.10 for 4 hours. There are 65 spaces, including two electric charging points. Great value. Well done Durham County Council!
Egglestone Abbey (formally the abbey of St Mary and St John the Baptist) was founded between 1195 and 1198 for Premonstratensian or ‘white’ canons. The only other abbey or priory of this order we have visited was in Kent, at Bayham Old Abbey.
The abbey was never prosperous, indeed quite small. It stands on a rise overlooking the Tees. English Heritage have a comprehensive history account on its website. A ground plan can be accessed here.
Today, the ruins comprise parts of the nave (with both Norman and Gothic doors), the outlines of the cloister and several other buildings, and the east range which was rebuilt in the 16th century, presumably after the Dissolution of the Monasteries. There is some particularly fine stonework.
I have posted more photos of the site and information boards in this album.
Then it was time to head home, a round trip of 120 miles.
The North Pennines National Landscape is truly spectacular, especially if the weather is good. Here is a video I made from my dashcam. It starts just before reaching Eggleston where we turned on to the B6278 to cross from Teesdale into Weardale, reaching almost 1700 feet at the highest point. It must be grim up there in mid-winter.
In July 2024 we’d visited High Force waterfall, further west up Teesdale from Barnard Castle, and crossed over from Teesdale to Weardale there. In this post you can view the video of that western route, as well as from Weardale to the Tyne Valley. We also took that latter route on our recent trip.







































 What we hadn’t done, until last week, was explore the hills southwest of Newcastle in the
What we hadn’t done, until last week, was explore the hills southwest of Newcastle in the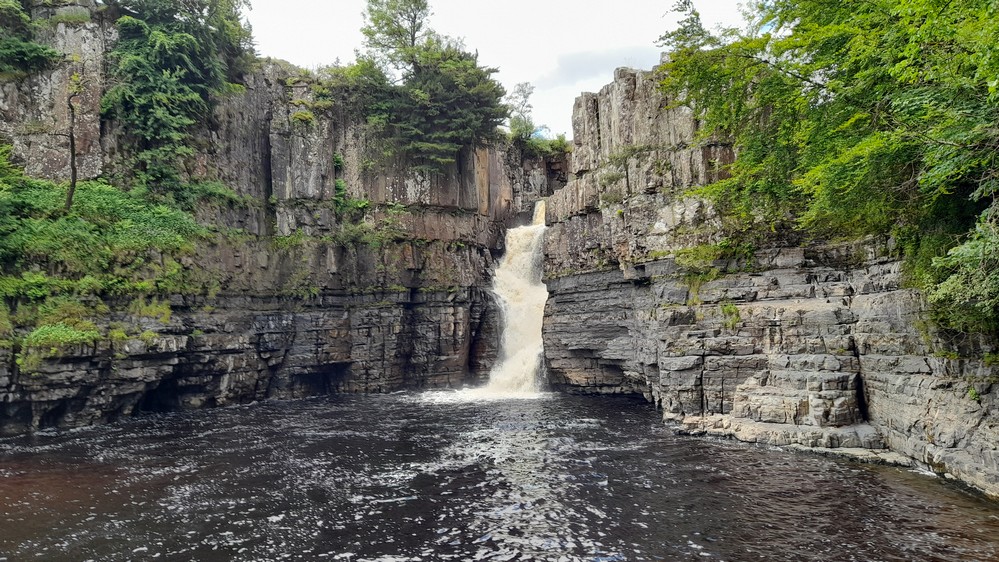 








 I was quite unaware of the waterfall’s existence until fairly recently, when I read a crime novel by Northumberland-born author
I was quite unaware of the waterfall’s existence until fairly recently, when I read a crime novel by Northumberland-born author 


