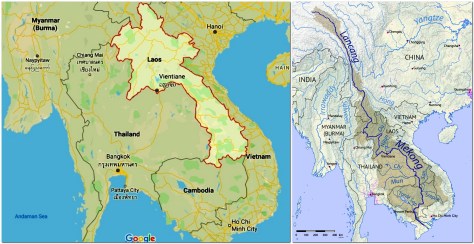
Laos or the Lao PDR (the Lao People’s Democratic Republic – actually a Unitary Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic) is one of the few landlocked countries in Asia. But it does have a connection to the sea, down the Mekong River where, through its mighty delta in Vietnam, it disgorges into the South China Sea. For a considerable length, the Mekong is the international border between Myanmar and Laos, and Thailand and Laos.
Laos or the Lao PDR (the Lao People’s Democratic Republic – actually a Unitary Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic) is one of the few landlocked countries in Asia. But it does have a connection to the sea, down the Mekong River where, through its mighty delta in Vietnam, it disgorges into the South China Sea. For a considerable length, the Mekong is the international border between Myanmar and Laos, and Thailand and Laos.
During the 19 years I spent in Asia (with the International Rice Research Institute in the Philippines) I visited Laos more than any other country, probably a couple of times a year over a five to six year period. Why? Because it was a focal country for the major rice conservation project that I managed between 1995 and 2000, funded by the Swiss government.
The Swiss, through the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC), also funded an in-country Lao-IRRI Program. So, as we were looking to strengthen the collection and conservation of indigenous rice varieties and wild rices in that country, it was a logical step to associate our rice biodiversity project administratively with the Lao-IRRI Project. The scientist who we hired for the Lao component of the project, Dr Seppana Appa Rao (originally from a sister center, ICRISAT, in Hyderabad, India) was based in the Lao capital Vientiane, and reported on a day-to-day basis to the leader of the Lao-IRRI Project, Australian agronomist Dr John Schiller (who passed away a couple of years ago).

Enjoying dinner with Appa Rao and John Schiller at John’s home in Vientiane.
In February 1997 I was joined on one of these visits to Laos by my wife Steph. IRRI had a generous travel policy. For every so many days a scientist was travelling outside the Philippines (but discounting the days of departure and arrival), his/her spouse or partner was entitled to one trip to a destination in Asia. So, we took advantage of that policy for a slightly extended visit to Laos (to take in some of the sights) as well as a weekend in Bangkok, through we had to transit in any case. A trip to Laos inevitably involved an overnight stop in Bangkok on both legs of the journey, taking a late flight out of Manila to Bangkok (about three hours) then the first flight on Thai Airways or Lao Aviation the next morning to Vientiane.
When I first visited Laos in 1995, the population of Vientiane was less than 400,000. It’s now reported at over 800,000. Back in the day it had the feel of a small town hugging the banks of the Mekong. But even then the traffic could become snarled at times. I wonder what it’s like nowadays? Looking at a satellite image the other day, the spread from the city center is clear. Even back in the 1990s, the city had begun to rapidly spread eastwards. The National Agricultural Research Center (NARC) of the National Agriculture and Forestry Research Institute (NAFRI) had its research station in this area, and where a rice genebank was constructed with financial support from the Swiss.
On this particular trip, Steph and I spent time with Appa and his Lao colleagues, Dr Chay Bounphanousay and Ms Kongphanh Kanyavong at the research center, looking at the genebank, field plots and various other facilities used to conserve the rice varieties collected throughout the country. This was also of interest for Steph as she originally trained in genetic resources, and has an MSc degree in genetic resources conservation and use from the University of Birmingham (where we met in 1971/72).

L-R: Kongphanh Kanyavong, Appa Rao, and Chay Bounphanousay
We also visited a research site where wild rices were being monitored in a joint project with Japanese scientists. It was hoped that data from that project would inform the establishment of field or in situ conservation sites around the country.
Driving around Vientiane as tourists, we noted that two buildings dominate the skyline in the city center. The first, the Patuxai monument, is a huge war memorial that commemorates the struggle for independence from France. The other, a short distance away to the northeast, is Pha That Luang, a large, gold covered Buddhist stupa.
And after a hard day in the field, or touring the city and markets, what better way to end the day than a stroll along the banks of the Mekong.

That’s Thailand on the far bank.
On another day, Appa, his wife, Chay, and Kongphanh took us for a boat excursion round the Nam Ngum Reservoir, about 70 km north of Vientiane, and afterwards to the Lao Zoo nearby.
Steph and I were also invited to participate in a Baci Ceremony at John’s home, which involves the tying of white cotton strings around person’s wrists and the prayer saying or well wishing for the person that the ceremony is intended for. I had been to one of these ceremonies before, during my first visit to Laos. Another new IRRI staff member, agronomist Bruce Linquist and his family, were also welcomed to Laos at this particular ceremony.
But the tourist highlight of our visit was a weekend in Luang Prabang (a 40 min flight north of Vientiane), an ancient city standing on a peninsula at the confluence of the Mekong and the Nam Khan River.
In 1997 there were few tourists in the city besides ourselves. As we walked through the streets of the ‘old town’ the locals we passed would smile and say hello, and go on about their business. They paid no attention to us whatsoever. Luang Prabang has become a mecca for tourists from afar, and must be a very different place nowadays.
After checking into our hotel (I don’t remember which one—it was new and on the southwest of the city center), we set out to explore the sights.
First on our list was the sixteenth century Buddhist temple Wat Xieng Thong, or Temple of the Golden City, at the northern end of the peninsula. It is one of the most important shrines in the country.
The architecture is breathtaking, and as we wandered around the temple, there was a just a feeling of serenity.
Later in the day before sunset, we climbed 100m high Phousi Hill to enjoy the 360° panorama from the summit, looking north over the old town and the Nam Khan River.
I guess the highlight of our trip to Luang Prabang was the 25 km or so boat trip we took upstream along the Mekong to visit the shrines at the Pak Ou Caves, which are opposite the mouth of the Ou River as it flows into the Mekong.
As I already mentioned, Luang Prabang was very quiet, and we hired a river boat to ourselves. The journey took about two hours, during which we had the chance to take in, close-up, the majesty of the Mekong.

At the landing stage where we took our boat. You can see several of these boats behind Steph, looking north along the Mekong.
Approaching the landing stage at Pak-Ou, our boatman carefully positioned his boat so that we could disembark safely. While we were ashore, he turned the boat around ready for the return, but also a short diversion into the mouth of the Ou River.
There are two caves: Tham Ting is the lower; Tham Phum is the upper. Both are filled with hundreds if not thousands of Buddha sculptures.
We were the only visitors on this day, and had the site to ourselves. Nowadays, it’s rather different as this photo (copied from the website http://www.viajeasean.com) clearly shows.

After a late afternoon meal overlooking the Mekong back in Luang Prabang, our visit to this ancient city came to an end, and we flew back to Vientiane the following morning, and on to Bangkok.