I believe it was IRRI’s former head of plant pathology Dr Tom (Twng-Wah) Mew who first coined this aphorism to describe IRRI’s philosophical approach to research (and I paraphrase):
It’s not only necessary to do the right science,
but to do the science right.
I couldn’t agree more, and have blogged elsewhere about the relevance of IRRI’s science. But this is science or research for development (or R4D as it’s often abbreviated) and best explained, perhaps by the institute’s tagline or slogan:

This is not science in a vacuum, in an ivory tower seeking knowledge for knowledge’s sake. This is research to solve real problems: to reduce poverty and increase food security. I don’t really like the distinction that’s often made between so-called pure or basic science, and applied science. Surely it’s a continuum? Let me give you just one example from my own research experience.
I have also blogged about the problem of bacterial wilt of potatoes. It can be a devastating disease, not only of potatoes and other solaneaceous crops like tomatoes and eggplants, but also of bananas. While the research I carried out was initially aimed at identifying better adapted potatoes resistant to bacterial wilt, very much an ‘applied’ perspective, we also had to investigate why the bacterium was surviving so long in the soil in the apparent absence of susceptible hosts. This epidemiological focus fed into better disease control approaches.
But in any case, the only distinction that perhaps really matters is whether the science is ‘good’ or ‘bad’.
Why is rice science so crucial? Because rice is the world’s most important staple food, feeding more than half of the global population on a daily basis, even several times a day in some Asian countries. IRRI’s science focuses on gains for rice farmers and those who eat rice, research that can potentially affect billions of people. It’s all about impact, at different levels. While not all impact is positive, however, it’s important to think through all the implications and direction of a particular line of research even before it starts. In other words ‘What does success look like?‘ and how will research outputs become positive outcomes?
Now I don’t claim to be an expert in impact assessment. That’s quite a specialized field, with its own methodologies. It wasn’t until I changed careers at IRRI in 2001 and became the Director for Program Planning and Communications (DPPC) that I fully came to understand (or even appreciate) what ex ante and ex post impact meant in the context of R4D. I was fortunate as DPPC to call upon the expertise of my Australian colleague, Dr Debbie Templeton, now back in her home country with the Australian Center for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR).
 Rice Science for a Better World?
Rice Science for a Better World?
IRRI has a prestigious scientific reputation, and deservedly so. It strives hard to maintain that reputation.
IRRI scientists publish widely in international journals. IRRI’s publication rate is second-to-none. On occasion IRRI has been criticized, censured almost, for being ‘obsessed with science and scientific publication’. Extraordinary! What for heaven’s sake does ‘Research’ in the name ‘International Rice Research Institute’ stand for? Or for that matter, in the name ‘CGIAR’ or ‘Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research’?
What our erstwhile colleagues fail to grasp, I believe, is that scientific publication is a consequence of doing good science, not an objective in itself. Having recruited some of the best scientists, IRRI provides an environment that brings out the best in its staff to contribute effectively to the institute’s common goals, while permitting them to grow professionally. Surely it must be the best of both worlds to have scientists contributing to a worthwhile and important research agenda, but knowing that their work is also esteemed by their scientific peers?
But what is the ‘right science’? Well, it depends of course.
IRRI is not an academic institution, where scientists are expected to independently pursue their own interests, and bring in large sums of research funding (along with the delicious overheads that administrators expect). All IRRI scientists contribute—as breeders, geneticists, pathologists, molecular biologists, economists, or whatever—to a common mission that:
. . . aims to reduce poverty and hunger, improve the health of rice farmers and consumers, and ensure environmental sustainability of rice farming. We do these through collaborative research, partnerships, and the strengthening of the national agricultural research and extension systems, or NARES, of the countries we work in.
IRRI’s research agenda and policies are determined by a board of trustees, guided by input from its partners, donors, end users such as farmers, and its staff. IRRI aims to meet five goals, aligned with the objectives of the Global Rice Science Partnership (GRiSP), that coordinates rice research among more than 900 international partners, to:
- Reduce poverty through improved and diversified rice-based systems.
- Ensure that rice production is stable and sustainable, does minimal harm to the environment, and can cope with climate change.
- Improve the nutrition and health of poor rice consumers and farmers.
- Provide equitable access to information and knowledge on rice and help develop the next generation of rice scientists.
- Provide scientists and producers with the genetic information and material they need to develop improved technologies and enhance rice production.
Rice Science for a Better World, indeed.
International agricultural research like IRRI’s is funded from the public purse, in the main, though the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation has become a major player supporting agricultural research over the past decade. Tax dollars, Euros, British pounds, Swiss francs, or Japanese yen are donated—invested even—through overseas development assistance budgets like USAID in the USA, the European Commission, DfID in the UK, SDC in Switzerland, and several institutions in Japan, to name just a handful of those donor agencies committed to finding solutions to real problems through research. Donors want to see how their funds are being used, and the positive benefits that their investments have contributed to. Unfortunately donors rarely share the same vision of ‘success’.
One of the challenges that faces a number of research organizations however, is that their research mandates fall short of effectively turning research outputs into research outcomes or impact. But having an idea of ‘what success looks like’ researchers can be in a better position to know who to partner with to ensure that research outputs become outcomes, be they national scientists, civil society organizations, NGOs, and the like.
As I said, when I became DPPC at IRRI, my office managed the process of developing and submitting research project funding proposals, as well as reporting back to donors what had been achieved. I had to get this message across to my research scientist colleagues: How will your proposed research project benefit farmers and rice consumers? This was not something they expected.
Quite early on in my DPPC tenure, I had a wake-up call after we had submitted a proposal to the Asian Development Bank (ADB), at their request I should add, to support some work on rice genomics. The science described in the proposal was first rate. After mulling over our proposal for a couple of months, I received a phone call from our contact at ADB in Manila who was handling the internal review of the proposal. He asked me to add a paragraph or two about how this work on rice genomics would benefit rice consumers otherwise ADB would not be able to consider this project in its next funding round.
So I went to discuss this apparent conundrum with the scientist involved, and explained what was required for ADB approval. ‘How will rice genomics benefit rice farmers and consumers?‘, I asked him. ‘I can’t describe that‘ he relied, somewhat woefully. ‘Well‘, I replied, ‘unless we can tell ADB how your project is going to benefit farmers etc, then your proposal is dead in the water‘.
After some thought, and based on my simplistic explanation of the impact pathway, he did come up with quite an elegant justification that we could submit to ADB. Despite our efforts, the project was not funded by ADB. The powers-that-be decided that the research was too far removed from the ultimate beneficiaries. But the process in itself was useful. It helped us to understand better how we should pitch our proposals and what essential elements to show we had thought things through.
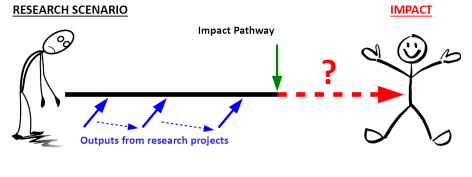
Now the graphic below is obviously a simplistic representation of a complex set of issues. The figure on the left represents a farmer, a community, a situation that is constrained in some way or other, such as low yield, diseased crops, access to market, human health issues, and the like. The objective of the research must be clearly defined and described. No point tilting at the wrong windmills.
The solid black and dashed red line represents the impact pathway to a better situation, turning research outputs into outcomes. The green arrow represents the point on that impact pathway where the research mandate of an institute often ends—before the outcome is delivered and adopted. How to fill that gap?
Individual research projects produce outputs along the impact pathway, and outputs from one project can be the inputs into another.
Whatever the impact pathway, it’s necessary to describe what success looks like, an increase in production over a specified area, release and adoption of disease resistant varieties, incomes of X% of farmers in region Y increased by Z%, or whatever.
Let me highlight two IRRI projects. One has already shown impact after a research journey of almost two decades. The other, perhaps on-going for the same time period, has yet to show impact. I’m referring to submergence tolerant or ‘scuba rice‘, and ‘Golden Rice’, respectively.
 For the development of scuba rice it was first necessary to identify and characterize genes conferring submergence tolerance—many years in the laboratory even before the first lines were tested in the field and the proof of concept realized. It didn’t take long for farmers to see the advantage of these new rice varieties. They voted with their feet! So, in a sense, the farmers themselves managed the dashed red line of the impact pathway. Scuba rice is now grown on more than 2.5 million hectares by 10 million farmers in India and Bangladesh on land that could not consistently support rice crops because of flooding.
For the development of scuba rice it was first necessary to identify and characterize genes conferring submergence tolerance—many years in the laboratory even before the first lines were tested in the field and the proof of concept realized. It didn’t take long for farmers to see the advantage of these new rice varieties. They voted with their feet! So, in a sense, the farmers themselves managed the dashed red line of the impact pathway. Scuba rice is now grown on more than 2.5 million hectares by 10 million farmers in India and Bangladesh on land that could not consistently support rice crops because of flooding.
 Golden Rice has the potential to eradicate the problem of Vitamin A deficiency, which can lead to blindness. As I mentioned earlier, rice is eaten by many people in Asia several times a day. It’s the perfect vehicle to enhance the Vitamin A intake. Varieties have been produced, the proof of concept completed, yet Golden Rice is not yet grown commercially anywhere in those countries that would benefit most. The dashed red line in my impact pathway diagram is the constraint. Golden Rice is a GMO, and the post-research and pre-release regulatory framework has not been surmounted. Pressure groups also have delayed the testing of Golden Rice lines, even destroying field experiments that would provide the very data they are so ‘afraid’ of. Thus its impact is more potential than real. Donors have been patient, but is there a limit to that patience?
Golden Rice has the potential to eradicate the problem of Vitamin A deficiency, which can lead to blindness. As I mentioned earlier, rice is eaten by many people in Asia several times a day. It’s the perfect vehicle to enhance the Vitamin A intake. Varieties have been produced, the proof of concept completed, yet Golden Rice is not yet grown commercially anywhere in those countries that would benefit most. The dashed red line in my impact pathway diagram is the constraint. Golden Rice is a GMO, and the post-research and pre-release regulatory framework has not been surmounted. Pressure groups also have delayed the testing of Golden Rice lines, even destroying field experiments that would provide the very data they are so ‘afraid’ of. Thus its impact is more potential than real. Donors have been patient, but is there a limit to that patience?
Keeping donors on-side
What I also came to realize early on is that it’s so necessary to engage on a regular basis with donors, establish a good working relationship, visit them in their offices from time-to-time, sharing a drink or a meal. Mutual confidence builds, and I found that I could pick up the phone and talk through an issue, send an email and get a reply quickly, and even consulted by donors themselves as they developed their funding priorities. It’s all part of research management. Donors also like to have ‘good news stories’. Nowadays, social media such as Facebook and Twitter, blogging even, also keep them in the loop. After all donors have their own constituencies—the taxpayers—to keep informed and onside as well.
Achieving impact is not easy. But if you have identified the wrong target, then no amount of research will bring about the desired outcome, or less likely to do so. While impact is the name of the game, good communications is equally important. They go hand-in-hand.












































 Many examples are highlighted in a recent article,
Many examples are highlighted in a recent article, 









 Finally, among the genetic resources experts,
Finally, among the genetic resources experts, 

 What about identical monozygotic twins, such as
What about identical monozygotic twins, such as 
 and the CGIAR
and the CGIAR
 Ron Cantrell, IRRI’s Director General in 2002 asked me to organize IRRI Day. But what to organize and who to involve? We decided very early on that, as much as possible, to show our visitors rice growing in the field, but with some laboratory stops where appropriate or indeed feasible, taking into account the logistics of moving a large number of people through relatively confined spaces.
Ron Cantrell, IRRI’s Director General in 2002 asked me to organize IRRI Day. But what to organize and who to involve? We decided very early on that, as much as possible, to show our visitors rice growing in the field, but with some laboratory stops where appropriate or indeed feasible, taking into account the logistics of moving a large number of people through relatively confined spaces.















































































 Sponsored by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), the 4th International Rice Congress brought together rice researchers from all over the world. Previous congresses had been held in Japan, India and last time, in 2010, in Hanoi, Vietnam (for which I also organized the science conference). This fourth congress, known as IRC2014 for short, had three main components:
Sponsored by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), the 4th International Rice Congress brought together rice researchers from all over the world. Previous congresses had been held in Japan, India and last time, in 2010, in Hanoi, Vietnam (for which I also organized the science conference). This fourth congress, known as IRC2014 for short, had three main components:








 Way back at the beginning of 2013 IRRI management asked me if I would like to organize the science conference in Bangkok, having taken on that role in 2009 before I retired from IRRI and for six months after I left. From May 2013 until IRC2014 was underway, I made four trips to the Far East, twice to Bangkok and three times to IRRI. We formed a
Way back at the beginning of 2013 IRRI management asked me if I would like to organize the science conference in Bangkok, having taken on that role in 2009 before I retired from IRRI and for six months after I left. From May 2013 until IRC2014 was underway, I made four trips to the Far East, twice to Bangkok and three times to IRRI. We formed a 



































































 My flight from Manila arrived quite late at night, and a vehicle and driver were sent to KL airport to pick me up. On the journey from the airport my driver became quite chatty. He asked where I was from, and when I told him I was working in the Philippines on rice, he replied ‘You must be working at IRRI, then‘ (
My flight from Manila arrived quite late at night, and a vehicle and driver were sent to KL airport to pick me up. On the journey from the airport my driver became quite chatty. He asked where I was from, and when I told him I was working in the Philippines on rice, he replied ‘You must be working at IRRI, then‘ (




 I was visiting in connection with the
I was visiting in connection with the 


 For rice, however, there is only one meeting of significance, and that’s the International Rice Congress, with the 4th Congress (IRC2014) scheduled to take place in Bangkok, Thailand from 27-31 October 2014. And I have been taken on as a consultant by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) to lead the development of the congress science program. Before I retired from IRRI in 2010 I had a similar role for the 3rd Congress (IRC2010) that was held in Hanoi, Vietnam in early November 2010. Planning had begun in early 2009, and after retiring I completed my role from my home in the UK.
For rice, however, there is only one meeting of significance, and that’s the International Rice Congress, with the 4th Congress (IRC2014) scheduled to take place in Bangkok, Thailand from 27-31 October 2014. And I have been taken on as a consultant by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) to lead the development of the congress science program. Before I retired from IRRI in 2010 I had a similar role for the 3rd Congress (IRC2010) that was held in Hanoi, Vietnam in early November 2010. Planning had begun in early 2009, and after retiring I completed my role from my home in the UK. The congress will be held at
The congress will be held at 








 Getting back to Christmas at IRRI. A number of staff take their annual leave from mid-December, especially those from the Antipodes, and parts of Asia. So it became a tradition for the Director General and his wife to host a Christmas party on the second Sunday of December, especially for all the children, and have Santa Claus make an appearance and distribute presents to one and all. One of the happiest responsibilities I had for about a decade was to dig out my Santa suit each year – and my make-up, and put in an appearance as Santa. From about mid-September onwards I’d let my beard and moustache grow so that by early December it was quite bushy. Although my hair and beard are mostly white now, a little make-up always added to the impression. During the 1990s, the role of Santa had been taken by my old friend, the late Bob Huggan, and then Bob Zeigler (now Director General) when he was a Program Leader.
Getting back to Christmas at IRRI. A number of staff take their annual leave from mid-December, especially those from the Antipodes, and parts of Asia. So it became a tradition for the Director General and his wife to host a Christmas party on the second Sunday of December, especially for all the children, and have Santa Claus make an appearance and distribute presents to one and all. One of the happiest responsibilities I had for about a decade was to dig out my Santa suit each year – and my make-up, and put in an appearance as Santa. From about mid-September onwards I’d let my beard and moustache grow so that by early December it was quite bushy. Although my hair and beard are mostly white now, a little make-up always added to the impression. During the 1990s, the role of Santa had been taken by my old friend, the late Bob Huggan, and then Bob Zeigler (now Director General) when he was a Program Leader.

 My predecessor at IRRI was Dr Te-Tzu Chang, known to everyone as ‘TT’. He joined IRRI in 1962 and over the years had built the germplasm collection to about 75,000 or so accessions by the time I joined the institute, as well as leading IRRI’s upland rice breeding efforts.
My predecessor at IRRI was Dr Te-Tzu Chang, known to everyone as ‘TT’. He joined IRRI in 1962 and over the years had built the germplasm collection to about 75,000 or so accessions by the time I joined the institute, as well as leading IRRI’s upland rice breeding efforts.





















 Botanist. That’s right. Not plant scientist or plant biologist. Botanist!
Botanist. That’s right. Not plant scientist or plant biologist. Botanist!





 Another influence was Missouri Botanical Garden geneticist Edgar Anderson. If you’ve not read his highly entertaining and readable Plants, Man & Life, then grab yourself a copy.
Another influence was Missouri Botanical Garden geneticist Edgar Anderson. If you’ve not read his highly entertaining and readable Plants, Man & Life, then grab yourself a copy.




 Ms. Genoveva ‘Eves’ Loresto passed away in Cebu on 5 April after a long battle with cancer.
Ms. Genoveva ‘Eves’ Loresto passed away in Cebu on 5 April after a long battle with cancer.





