I’m fascinated by canals. You have to admire the visionaries who financed and built the canals, and the armies of men who constructed them.
Most canals in England and Wales were dug by gangs of navvies in the 18th and early 19th centuries. However, within just a generation or two the canals were already in decline as an expanding railway network made transportation of goods cheaper and faster. The writing was on the wall for the canals once George Stephenson had demonstrated the power of steam locomotion.
 The economic justification for and value of the canals waned, and they fell into disuse, and no longer navigable. However, in recent decades there has been a resurgence in the use of inland waterways. Today some 2000 miles of navigable waterways (canals and rivers) are managed by the Canal & River Trust, used mainly for pleasure traffic. Narrowboat holidays on the canals are very popular.
The economic justification for and value of the canals waned, and they fell into disuse, and no longer navigable. However, in recent decades there has been a resurgence in the use of inland waterways. Today some 2000 miles of navigable waterways (canals and rivers) are managed by the Canal & River Trust, used mainly for pleasure traffic. Narrowboat holidays on the canals are very popular.
I have written several stories about the pleasure Steph and I take from walking along the towpath of the Worcester & Birmingham Canal, that runs north-south between Gas Street Basin in the center of Birmingham and the River Severn at Worcester. The canal is less than two miles east of our home in Bromsgrove in north Worcestershire. Our walks normally cover small sections of the towpath between Tardebigge Top Lock (No. 58) and Astwood Bottom Lock (No. 17), a distance of about 5½ miles.
We not only enjoy the surrounding countryside, tranquil for the most part (unless a mainline express is speeding by about half a mile to the west), but also watching the canal narrowboats navigating their way up and down the Tardebigge Flight, the longest flight (of 30 locks) in the country, some with a greater degree of proficiency than others. Some days it can be like Piccadilly Circus¹ with boats queuing up to pass through the locks.
Taking to the water
We have taken only one canal holiday, in the summer of 1983, when Steph, Hannah (just five years old), Philippa (15 months) and me took to the water for a week, to navigate the Stourport Ring.
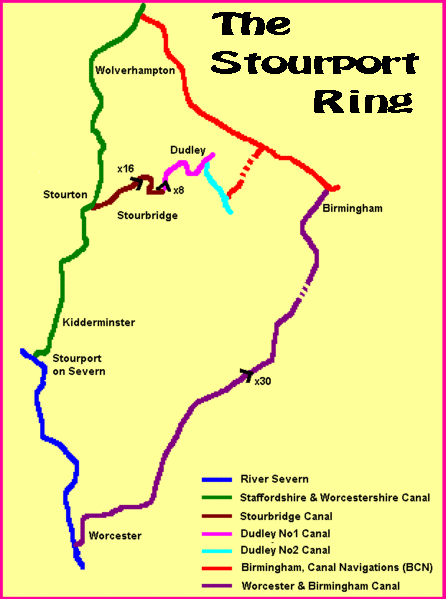
The Ring, for our purposes, comprised four waterways:
- the Worcester & Birmingham Canal (purple on the map below), between Birmingham and Worcester;
- The River Severn (blue), between Worcester and Stourport-on-Severn;
- The Staffordshire & Worcestershire Canal (green), from Stourport-on-Severn to Aldersley Junction; and
- the Birmingham Main Line Canal (red, part of the Birmingham Canals Navigation, BCN), from Aldersley Junction to Gas Street Basin.
If I remember correctly, the various links connecting the Staffordshire & Worcestershire Canal with the BCN via the Stourbridge Canal and the Dudley Canals were not navigable in 1983.
Setting out, and setting some rules
It was early July, and we took Hannah out of school for the week with readily-granted permission from Mr Richards, the headmaster at Finstall First School. That would be almost impossible nowadays. We had chosen a small, 4-berth narrowboat for our holiday, Blue Heron, from a hire-boat center operating out of Alvechurch, about 15 minutes from home. So, packing clothes for a week, and several boxes of groceries (including the inevitable wine boxes that were very popular in the 80s), we headed to Alvechurch to board our boat.
After a familiarization tour of the boat, one of the marina staff joined us for the first three miles to the first lock on our trip, Tardebigge Top Lock. Not only would that be the first lock we’d encounter over the next week, but it was one of the deepest. So, the marina staff not only wanted to guide us safely through this lock but also to show us the rudiments of safe canal navigation.

Looking at the various photos I have included in this post, you might be forgiven for questioning our apparent lack of awareness of on-board safety. Only Hannah is wearing a life jacket, something that would not be allowed more than three decades later. At five years old, we had to set Hannah some strict limits how to move around the boat. At 15 months, Philippa was already walking, and would crawl and stagger around the cabin whenever we moored for a meal break or at night. With either Steph or me steering the boat, one of us had to operate the locks, raising/ lowering the paddles to empty or fill each lock, and open the lock gates. So it was important we knew where the girls were at all times.
To keep Philippa safe, we put her in a high chair in the bow of the boat, and with her mob cap for protection, and a good coating of sun cream, she was (mostly) quite happy watching the world go by at a leisurely 4 mph (the maximum speed permitted on the canals), waving to passers-by, or falling asleep when the fancy took her. Hannah would often sit beside whoever was steering at the stern of the boat, or ‘help’ with the locks.
Our journey continues
Having successfully passed through Tardebigge Top Lock, we headed down a few more on our own, before mooring for the night just below the Engine House, then a nightclub/restaurant (but now converted into luxury apartments), near Lock 55 or 54, in the early evening. With two small children on board, we had to get them fed and not too late bedded down for the night.

Looking south on the Worcester & Birmingham Canal near Lock 54. The Malvern Hills can be seen in the far distance.
We spent all the next day completing the Tardebigge flight, but I’m not sure if we reached Worcester that same day, or took another day. Probably the latter. However, we spent one night at Worcester’s Diglis Basin before facing the River Severn.
It had become clear on the final stretch into Worcester that Hannah was not her usual perky self. And by bedtime, she had a temperature. The next morning she really looked very unwell, so she and I headed off into the center of Worcester in search of medical help. Although only 15 miles or so from home, it felt like 100 miles. I didn’t have our doctor’s telephone number with me. In any case, there were no mobile phones in 1983.
Nevertheless, we finally got to see a doctor (after completing a slew of NHS forms because we were being treated as ‘visitors’, not our own doctor), who diagnosed tonsillitis, and prescribed a course of antibiotics. It was remarkable how quickly those had an effect, because by late afternoon Hannah was feeling very much better, and almost back to her normal self by bedtime.
Our departure from Worcester was delayed until after lunch. We steeled ourselves for the section of our trip on the River Severn. We had good weather (and for the whole week), and no particular difficulties on the river itself. But we did have to pass through the Diglis Lock connecting Diglis Basin with the River Severn. This lock is wide and deep, and a challenge for two canal novices like Steph and myself. I don’t remember that this lock was assisted.
Once on the Severn we turned north, having a grandstand view from the center of the river of Worcester Cathedral on the east bank, and the city center.
There was just one other lock on the Severn itself, at Holt, to bypass a weir. That lock had lock keepers, and was electrically operated. Once we reached Stourport-on-Severn, it was time to leave the river and join the Staffordshire & Worcestershire Canal, for the next stage of our trip.
This canal passes through the center of Kidderminster, a town famous world-wide for its carpet-making industry, then on through some lovely and peaceful red sandstone landscapes near Kinver in South Staffordshire.
We must have taken a couple of days to travel this section as far as Aldersley Junction, where we had to turn east and join the Birmingham Canals Navigation. However, as we needed water and some other supplies, we travelled a couple of miles further north, joining the Shropshire Union Canal at Autherley Junction for a very short distance before turning around to moor up for the night by Aldersley Junction. At Autherley Junction, there is a stop lock, with just a small height difference, a matter of inches, between the two canals to prevent drainage of one canal into the other.
The next section on the BCN was our penultimate day, taking us from Aldersley Junction, through the Black Country, Birmingham city center, and south again on to the Worcester & Birmingham Canal, mooring up north of Alvechurch in order to arrive back on time at the marina the next day.
From Aldersley Junction there is a flight of 21 locks that raise the canal 132 feet. We made an early start, with the idea of stopping about half way for breakfast. However, we discovered at about one third of the climb that a previous boat had left the lock paddles open and several pounds between the locks had drained completely. The photo below was taken on the Worcester & Birmingham Canal a couple of years ago when several refurbishment projects were underway. But it shows the sort of scene that greeted us that morning on the BCN. It must have taken an hour or more to restore water levels to the pounds before we could get on the move once again.
Travelling between Wolverhampton and Birmingham in 1983 was like passing through a desolate lunar landscape, with scenes of dereliction all around. This is part of the so-called Black Country of Dudley and Tipton, formerly an important industrial area. Today this whole area has been reclaimed for housing. Even the derelict warehouses along the canals in the center of Birmingham have either been refurbished as ‘desirable residences’ or demolished and replaced by new housing and offices.
However in 1983, there was little shade along the banks of the BCN in the Black Country of Dudley and Tipton. It was a very hot day, and the sun was beating down. Because we had to travel more miles than usual, I had my lunch and tea breaks on the move, so to speak. Just as we crossed Gas Street Basin, the weather broke and there was a tremendous thunderstorm. With that, we decided to moor until the storm had passed, before continuing south, past the University of Birmingham Edgbaston campus, and through the one and a half mile long Wast Hills Tunnel (under the Lickey Hills) north of Alvechurch, one of the longest in the country. We moored close to where the A441 crosses the canal at Hopwood, and enjoyed an evening meal at the Hopwood House pub.
With only a short distance to Alvechurch, we spent a couple of hours cleaning the boat on the final morning, getting everything shipshape and Bristol fashion, and arriving back at the marina by the noon deadline.
From there, it was just a case of hopping into our car, and within 15 minutes we were back home. A very enjoyable holiday and, as you can tell as you read this post, one that left me with long-lasting memories.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
¹ The phrase it’s like Piccadilly Circus is commonly used in the UK to refer to a place or situation which is extremely busy with people.






























































 Per Ardua Ad Alta
Per Ardua Ad Alta My first visit to the university was in May or June 1967—to sit an exam. Biology was one of the four subjects (with Geography, English Literature, and General Studies) I was studying for my
My first visit to the university was in May or June 1967—to sit an exam. Biology was one of the four subjects (with Geography, English Literature, and General Studies) I was studying for my 





 in the Second Year. With my colleague Brian Ford-Lloyd (with whom I’ve published three books on genetic resources) I developed a Third Year module on genetic resources that seems to have been well-received (from some subsequent feedback I’ve received). I also contributed to a plant pathology module for Third Year students. But the bulk of my teaching was to MSc students on the graduate course on Conservation and Utilization of Plant Genetic Resources – the very course I’d attended a decade earlier. My main focus was crop evolution, germplasm collecting, and agricultural systems, among others. And of course there was supervision of
in the Second Year. With my colleague Brian Ford-Lloyd (with whom I’ve published three books on genetic resources) I developed a Third Year module on genetic resources that seems to have been well-received (from some subsequent feedback I’ve received). I also contributed to a plant pathology module for Third Year students. But the bulk of my teaching was to MSc students on the graduate course on Conservation and Utilization of Plant Genetic Resources – the very course I’d attended a decade earlier. My main focus was crop evolution, germplasm collecting, and agricultural systems, among others. And of course there was supervision of 








 Finally, among the genetic resources experts,
Finally, among the genetic resources experts,  Humble? Boiled, mashed, fried, roast, chipped or prepared in many other ways, the potato is surely the King of Vegetables. And for 20 years in the 1970s and 80s, potatoes were the focus of my own research.
Humble? Boiled, mashed, fried, roast, chipped or prepared in many other ways, the potato is surely the King of Vegetables. And for 20 years in the 1970s and 80s, potatoes were the focus of my own research.







 While I knew that Lynne spent most of his time producing hit albums for other musicians, and writing new material, I hadn’t realized how unpopular ELO had become since their heyday in the 70s. Apparently
While I knew that Lynne spent most of his time producing hit albums for other musicians, and writing new material, I hadn’t realized how unpopular ELO had become since their heyday in the 70s. Apparently 










 When the late
When the late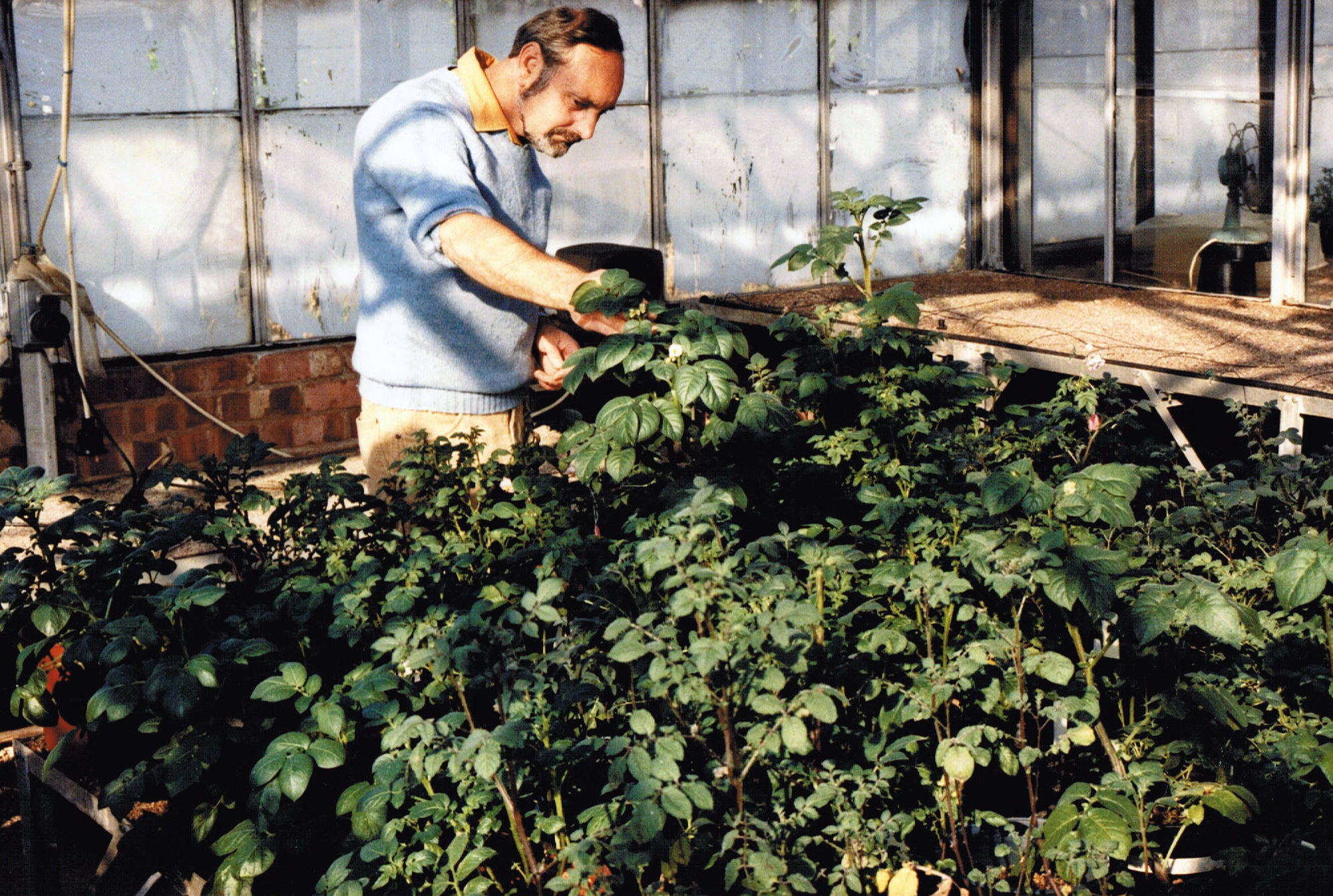 
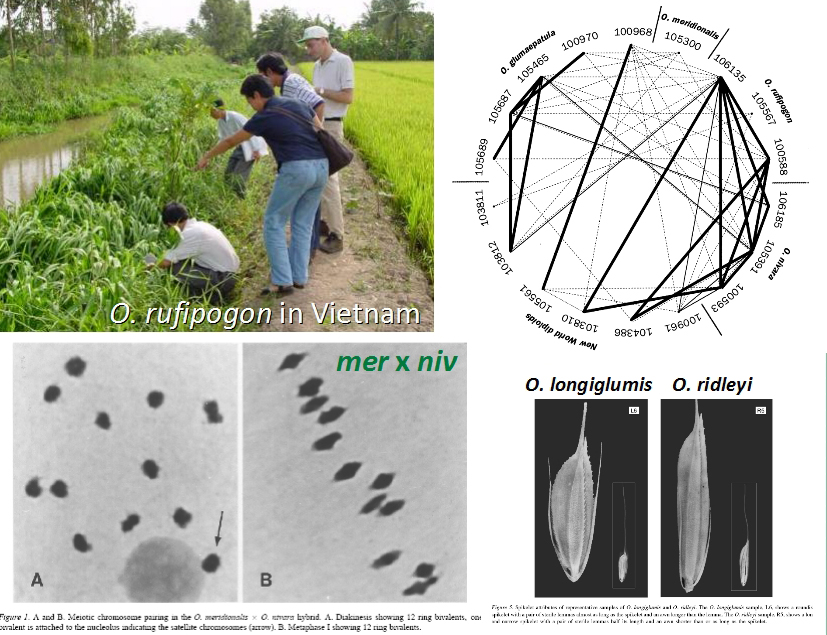
 Here is the list of University of Birmingham PhD students who worked on potatoes, as far as I can remember. All of them from 1975 (with the exception of Ian Gubb) had also attended the MSc course on genetic resources:
Here is the list of University of Birmingham PhD students who worked on potatoes, as far as I can remember. All of them from 1975 (with the exception of Ian Gubb) had also attended the MSc course on genetic resources: Richard Lester (UK), 1962. Taught at Makerere University in Uganda, before joining the Dept. of Botany at Birmingham in 1969. Retired in 2002, and died in 2006. Studied the biochemical systematics of Mexican wild Solanum species. The species Solanum lesteri is named after him.
Richard Lester (UK), 1962. Taught at Makerere University in Uganda, before joining the Dept. of Botany at Birmingham in 1969. Retired in 2002, and died in 2006. Studied the biochemical systematics of Mexican wild Solanum species. The species Solanum lesteri is named after him.
 Katsuo Armando Okada (Argentina), 1970 (?). Retired. Was with IBPGR for a while in the 1980s (?) in Colombia. Studied the origin of Solanum x rechei from Argentina.
Katsuo Armando Okada (Argentina), 1970 (?). Retired. Was with IBPGR for a while in the 1980s (?) in Colombia. Studied the origin of Solanum x rechei from Argentina.


 David Astley (UK), 1975. Became the curator of the vegetable genebank at Wellesbourne (now the
David Astley (UK), 1975. Became the curator of the vegetable genebank at Wellesbourne (now the 
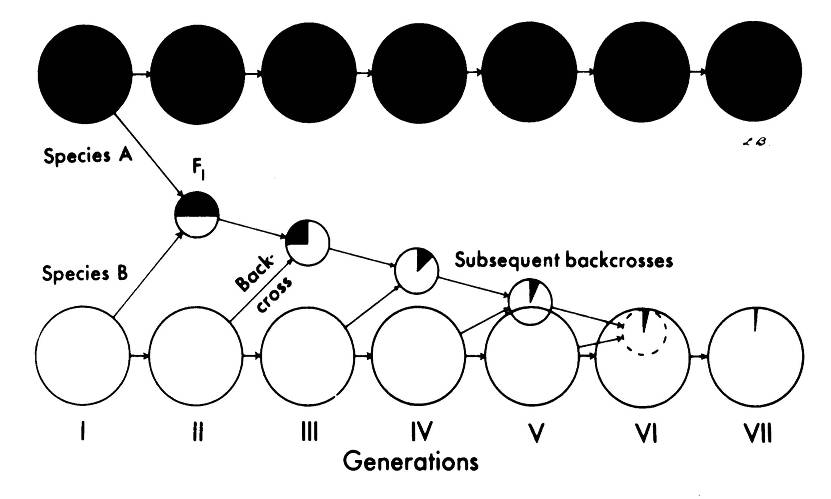
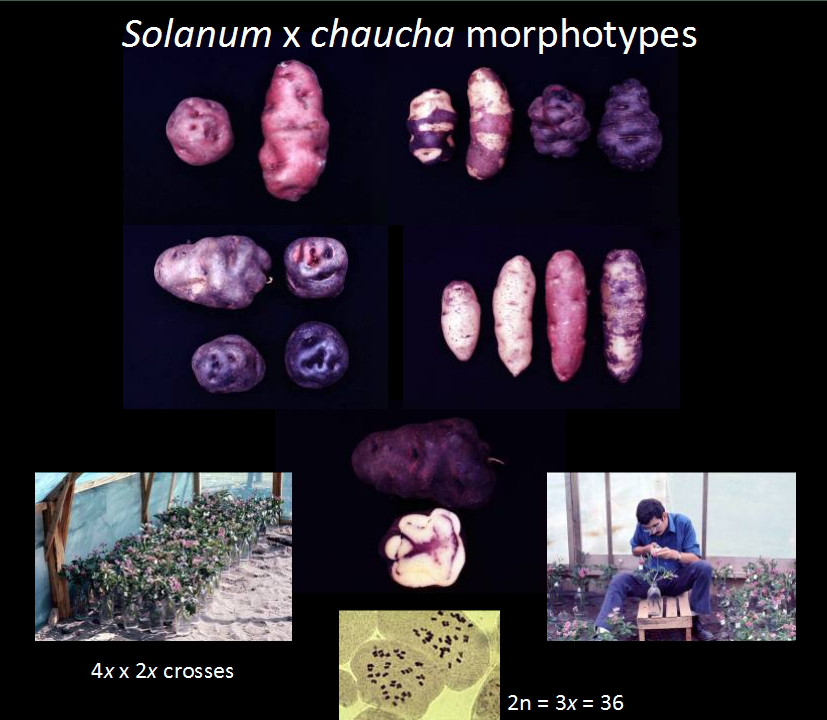
 Peter Schmiediche (Germany), 1977. He continued working with CIP as a potato breeder (for resistance to bacterial wilt), and was later CIP’s regional leader based in Indonesia. Now retired and sharing his time between Texas (where his children settled) and his native Berlin. Studied the bitter potatoes Solanum x juzepczukii (3x) and S. x curtilobum (5x). Joint with CIP and Roger Rowe.
Peter Schmiediche (Germany), 1977. He continued working with CIP as a potato breeder (for resistance to bacterial wilt), and was later CIP’s regional leader based in Indonesia. Now retired and sharing his time between Texas (where his children settled) and his native Berlin. Studied the bitter potatoes Solanum x juzepczukii (3x) and S. x curtilobum (5x). Joint with CIP and Roger Rowe. Carlos Arbizu (Peru), 1990. An expert on minor Andean tuber crops, he came from the University of Ayacucho. Spent time working in the germplasm program at CIP. Studied the origin and value of resistance to spindle tuber viroid in Solanum acaule. Joint with CIP and principal virologist Luis Salazar (who gained his PhD while studying at the
Carlos Arbizu (Peru), 1990. An expert on minor Andean tuber crops, he came from the University of Ayacucho. Spent time working in the germplasm program at CIP. Studied the origin and value of resistance to spindle tuber viroid in Solanum acaule. Joint with CIP and principal virologist Luis Salazar (who gained his PhD while studying at the  Susan Juned (UK), 1994. Now a sustainable technology consultant, Sue is an active local government councillor, and has stood for election to parliament on a couple of occasions for the Liberal Democrats. Studied
Susan Juned (UK), 1994. Now a sustainable technology consultant, Sue is an active local government councillor, and has stood for election to parliament on a couple of occasions for the Liberal Democrats. Studied  David Tay (Malaysia), 2000. He worked in Australia and then was Director of the USDA Ornamental Plant Germplasm Center in Columbus, Ohio, but returned to CIP as head of the genetic resources unit in 2007. He’s now left CIP. I think he worked on diploid cultivated species. Joint with CIP. Not sure why his PhD is dated 2000, as he’d been in CIP in the late 70s.
David Tay (Malaysia), 2000. He worked in Australia and then was Director of the USDA Ornamental Plant Germplasm Center in Columbus, Ohio, but returned to CIP as head of the genetic resources unit in 2007. He’s now left CIP. I think he worked on diploid cultivated species. Joint with CIP. Not sure why his PhD is dated 2000, as he’d been in CIP in the late 70s.
 Roger Rowe, who had been in charge of the
Roger Rowe, who had been in charge of the 
 In preparation for Birmingham, I’d been advised to purchase and absorb a book that was published earlier that year, edited by Sir Otto Frankel and Erna Bennett [1] on genetic resources, and dedicated to NI Vavilov. And I came across Vavilov’s name for the first time in the first line of the Preface written by Frankel, and in the first chapter on Genetic resources by Frankel and Bennett. I should state that this was at the beginning of the genetic resources movement, a term coined by Frankel and Bennett at the end of the 60s when they had mobilized efforts to collect and conserve the wealth of diversity of crop varieties (and their wild relatives) – often referred to as landraces – grown all around the world, but were in danger of being lost as newly-bred varieties were adopted by farmers. The so-called Green Revolution had begun to accelerate the replacement of the landrace varieties, particularly among cereals like wheat and rice.
In preparation for Birmingham, I’d been advised to purchase and absorb a book that was published earlier that year, edited by Sir Otto Frankel and Erna Bennett [1] on genetic resources, and dedicated to NI Vavilov. And I came across Vavilov’s name for the first time in the first line of the Preface written by Frankel, and in the first chapter on Genetic resources by Frankel and Bennett. I should state that this was at the beginning of the genetic resources movement, a term coined by Frankel and Bennett at the end of the 60s when they had mobilized efforts to collect and conserve the wealth of diversity of crop varieties (and their wild relatives) – often referred to as landraces – grown all around the world, but were in danger of being lost as newly-bred varieties were adopted by farmers. The so-called Green Revolution had begun to accelerate the replacement of the landrace varieties, particularly among cereals like wheat and rice. Vavilov died of starvation in prison at the relatively young age of 55, following persecution under Stalin through the shenanigans of the charlatan Trofim Lysenko. Lysenko’s legacy also included the rejection of Mendelian genetics in the Soviet Union for many years. Eventually Vavilov was rehabilitated, long after his death, and he was commemorated on postage stamps at the time of his centennial.
Vavilov died of starvation in prison at the relatively young age of 55, following persecution under Stalin through the shenanigans of the charlatan Trofim Lysenko. Lysenko’s legacy also included the rejection of Mendelian genetics in the Soviet Union for many years. Eventually Vavilov was rehabilitated, long after his death, and he was commemorated on postage stamps at the time of his centennial. First,
First, 

 During the late 1980s, when I was on the faculty of the University of Birmingham, my colleague, Brian Ford-Lloyd (now Emeritus Professor of Conservation Genetics) and I had a research grant from United Biscuits to work on somaclonal variation in potatoes. Whatever is that? I hear you cry. Well, it’s technique to grow plants from small pieces of plant tissue on sterile nutrient agar (a jelly-like substance), and try and bring about genetic changes which are primarily due to disorganized tissue growth and chromosome changes. The plants thus produced are called somaclones. And our aim was to produce a somaclonal variant of the potato variety Record, which was at that time, one of the most important varieties for producing potato crisps (chips in American parlance).
During the late 1980s, when I was on the faculty of the University of Birmingham, my colleague, Brian Ford-Lloyd (now Emeritus Professor of Conservation Genetics) and I had a research grant from United Biscuits to work on somaclonal variation in potatoes. Whatever is that? I hear you cry. Well, it’s technique to grow plants from small pieces of plant tissue on sterile nutrient agar (a jelly-like substance), and try and bring about genetic changes which are primarily due to disorganized tissue growth and chromosome changes. The plants thus produced are called somaclones. And our aim was to produce a somaclonal variant of the potato variety Record, which was at that time, one of the most important varieties for producing potato crisps (chips in American parlance).



